Introduction
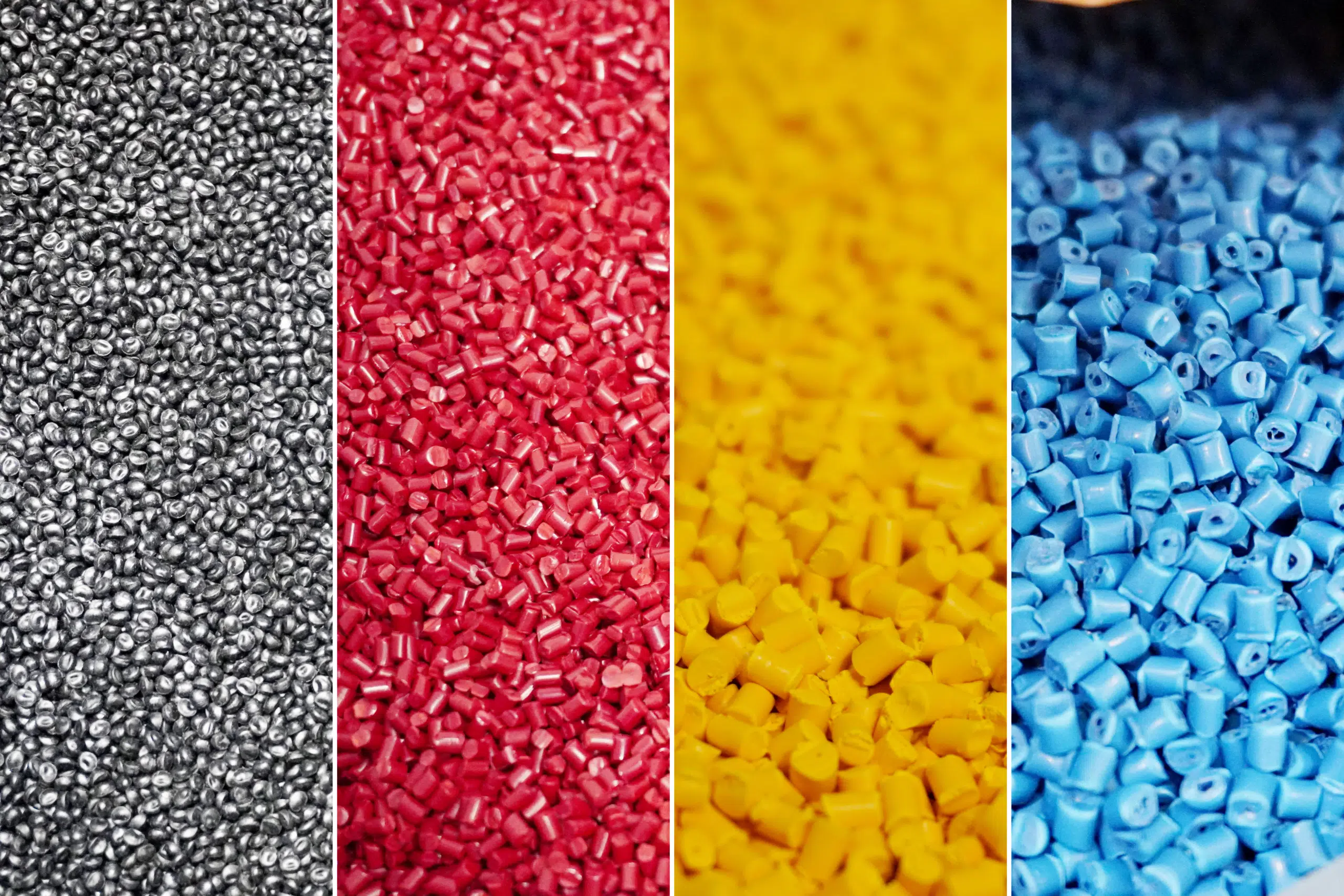
Polystyrene (PS) is one of the most versatile thermoplastics used across industries — from packaging and electronics to household goods and automotive components. Its clarity, rigidity, and ease of molding make it a preferred choice for a variety of applications. However, in its natural form, polystyrene is typically colorless and slightly brittle. This is where polystyrene pigments come into play. These colorants not only bring vibrancy and visual appeal to PS products but also enhance their durability and functional performance.
What Are Polystyrene Pigments?
Polystyrene pigments are finely dispersed coloring agents designed specifically for use in PS and its derivatives such as GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) and HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene). They can be organic or inorganic, each offering distinct color ranges and properties.
Organic pigments, such as azo or phthalocyanine types, provide bright and vivid hues, making them ideal for consumer goods and packaging materials. Inorganic pigments, like iron oxides and titanium dioxide, are valued for their superior opacity, heat resistance, and long-term color stability — key requirements in industrial or outdoor applications.
Because polystyrene has a relatively low processing temperature compared to other plastics, pigment selection must take into account thermal stability and dispersion quality, ensuring that the pigment does not degrade or cause color streaks during molding or extrusion.
Pigments for Different Types of Polystyrene
Polystyrene exists in multiple forms, each with unique performance needs that influence pigment choice:
-
GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) is known for its transparency and stiffness. It is used for clear or translucent parts like disposable cups, light diffusers, and cosmetic packaging. Pigments for GPPS must maintain high clarity and low haze. Transparent dyes or specially designed organic pigments are often used to achieve these effects.
-
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) contains rubber particles to improve toughness. Because it is opaque, the pigments used in HIPS must provide strong hiding power and good dispersion to prevent color inconsistency. Inorganic pigments are commonly preferred for this application.
For companies working with other plastic materials such as polyolefins, pigment formulation and compatibility also vary. (Learn more about pigments suitable for polyolefin materials here: Polyolefin Pigments.
Key Factors in Choosing Polystyrene Pigments
Selecting the right pigment system for polystyrene involves balancing color performance, processing requirements, and end-use conditions. Some of the most important factors include:
-
Heat Resistance
Pigments must withstand the heat of the injection molding or extrusion process (typically around 180–250°C). Poor heat stability can lead to fading or discoloration, especially for light or bright shades. -
Light and UV Stability
When PS products are exposed to sunlight, ultraviolet radiation can cause yellowing or fading. UV-stabilized pigments or those with additional light absorbers help maintain color consistency over time. -
Chemical Resistance
In packaging and industrial uses, polystyrene may contact cleaning agents, solvents, or oils. Pigments with strong chemical resistance prevent surface discoloration and degradation. -
Dispersion Quality
Uniform pigment dispersion ensures even coloring and consistent product appearance. High-quality masterbatch production is crucial to avoid color streaks or specks. -
Regulatory Compliance
For applications in food packaging or toys, pigments must comply with international safety regulations such as RoHS, REACH, and FDA standards. Selecting certified materials ensures both compliance and consumer safety.
Applications of Polystyrene Pigments
Polystyrene pigments are used across a wide range of industries thanks to their adaptability and aesthetic value:
-
Consumer Packaging – Used in food trays, cups, and cosmetic containers for visual appeal and brand differentiation.
-
Electronics – Coloring casings for appliances and devices while maintaining dimensional stability.
-
Automotive – Enhancing interior trims, knobs, and panels with durable and fade-resistant colors.
-
Household Products – From hangers and storage boxes to decorative items, polystyrene pigments provide vivid and lasting finishes.
In each case, pigment compatibility with the polymer matrix ensures the product retains its strength, gloss, and surface integrity.
Advantages of Using High-Quality Polystyrene Pigments
High-performance pigments deliver several critical benefits for manufacturers and end-users alike:
-
Improved Aesthetic Appeal: Vibrant and consistent colors elevate brand recognition and consumer perception.
-
Enhanced Product Lifespan: Pigments with UV and thermal stability maintain appearance over time.
-
Processing Efficiency: Well-dispersed pigments reduce waste and enhance molding consistency.
-
Customization Flexibility: Tailored pigment formulations allow for specific color matching and performance requirements.
These advantages contribute not only to product performance but also to cost efficiency and sustainability, as longer-lasting colors reduce the need for reprocessing or replacement.
Conclusion
Polystyrene pigments play a crucial role in transforming PS from a clear, neutral polymer into a colorful, functional material suited for diverse applications. Understanding pigment properties, compatibility, and processing behavior helps manufacturers achieve the perfect balance between color quality, performance, and production efficiency.
By selecting the right pigment system — whether organic or inorganic, transparent or opaque — producers can enhance both the aesthetic and functional value of their polystyrene products. For those working across different polymers, such as polyolefins or rubber-based materials, aligning pigment choice with the substrate’s chemistry ensures long-term stability and superior results.