A Technical Perspective on Pigment Behavior in Formulations
In industrial applications such as coatings, plastics, and inks, pigment performance depends not only on chemical composition, but also on how effectively pigments are dispersed within a formulation. Even high-quality pigments can fail to deliver expected color strength, gloss, or durability if dispersion quality is inadequate.
This article explains why dispersion quality is a critical factor in determining the final appearance, stability, and performance of industrial pigments, from a technical and application-oriented perspective.
Understanding Pigment Dispersion
Pigments are insoluble solid particles that must be uniformly distributed within a liquid or molten medium to function effectively. In their raw form, pigment particles tend to form agglomerates due to strong inter-particle forces such as van der Waals attraction.
Dispersion is the process of breaking down these agglomerates into smaller units and stabilizing them throughout the system. A well-dispersed pigment system ensures that pigment particles are evenly separated, allowing them to interact optimally with light and the surrounding binder.
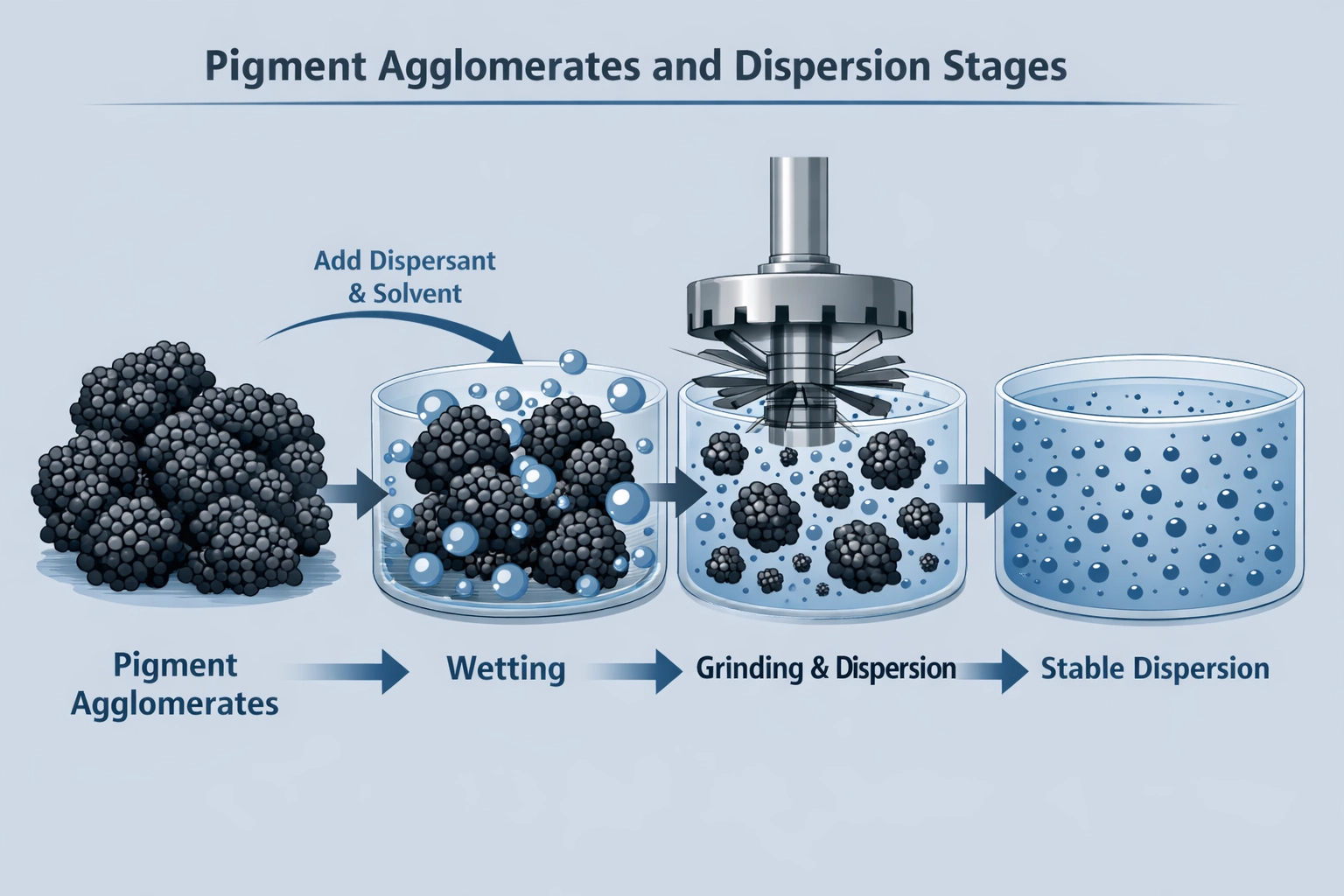
The Key Stages of Pigment Dispersion
Industrial pigment dispersion typically involves four interconnected stages:
-
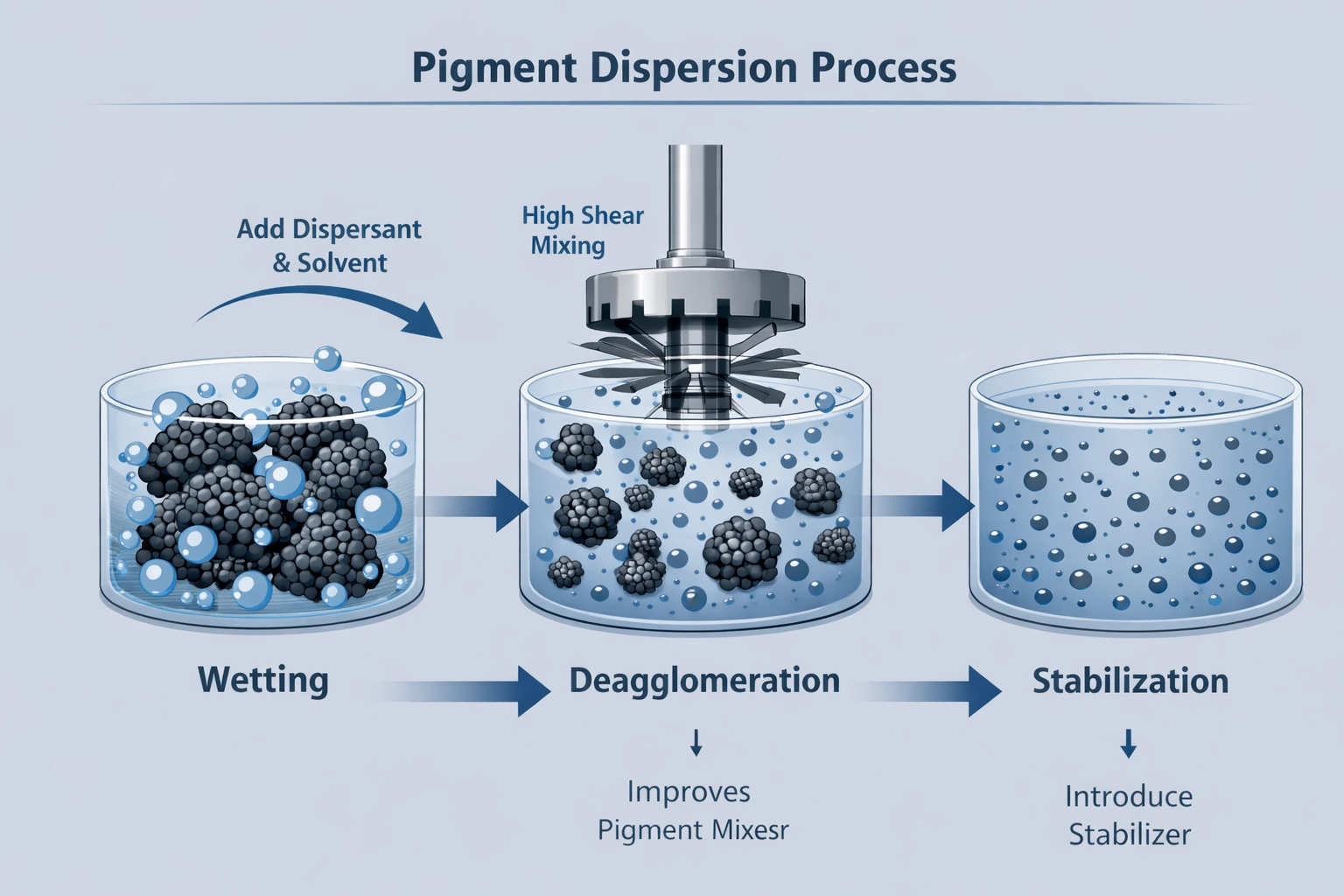
Wetting
The liquid medium (resin, solvent, or polymer melt) replaces air on the pigment surface. Proper wetting reduces surface energy and allows the medium to penetrate pigment agglomerates. -
Deagglomeration (Breaking Down)
Mechanical energy—generated by bead mills, high-speed mixers, or extruders—breaks large agglomerates into smaller aggregates or near-primary particles. -
Distribution
Pigment particles are evenly distributed throughout the formulation, minimizing local concentration differences. -
Stabilization
Dispersants or surface treatments prevent pigment particles from re-agglomerating, maintaining long-term dispersion stability.
Each stage directly influences the pigment’s optical and physical performance in the final product.
Impact of Dispersion on Color Strength and Hue
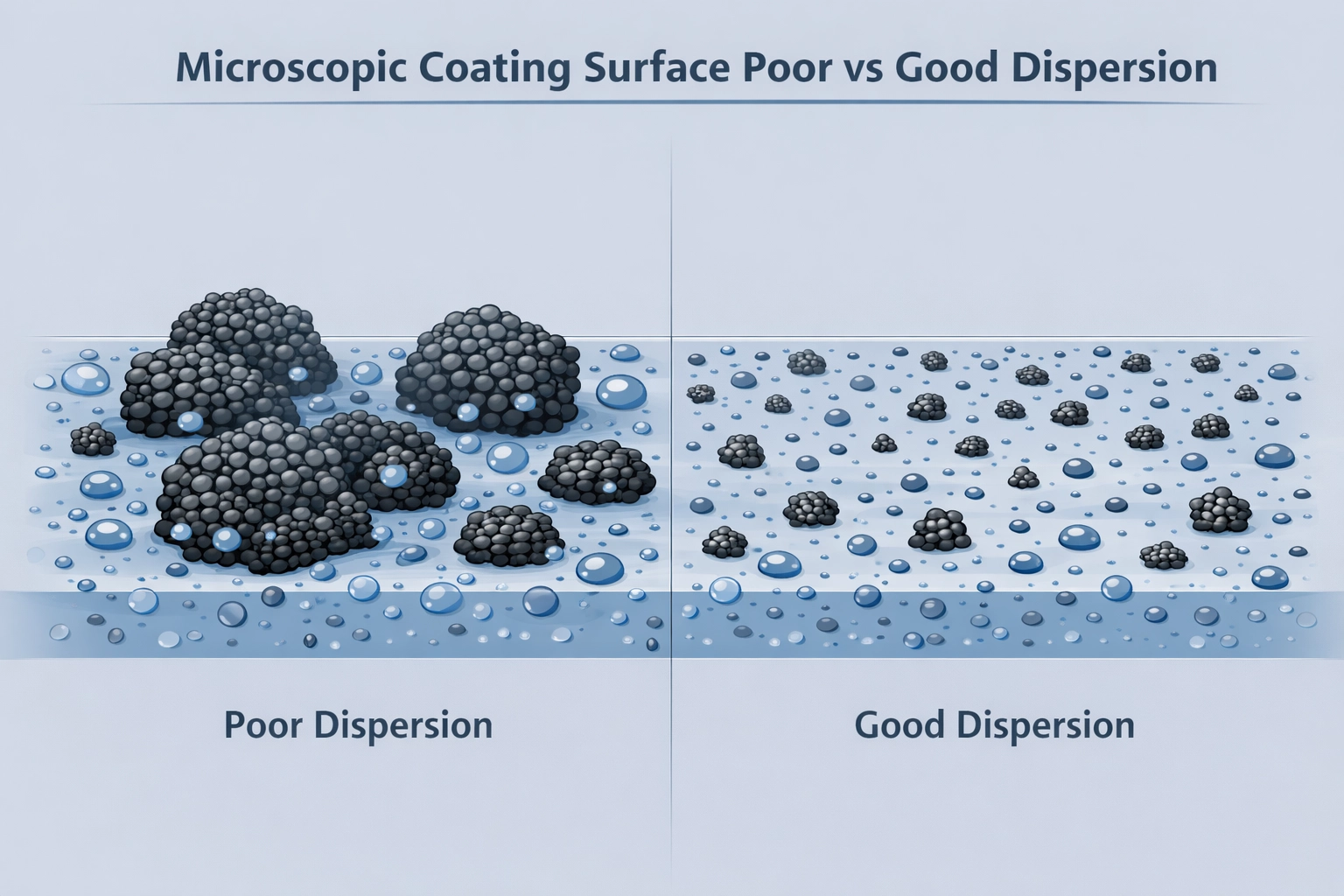
Dispersion quality has a direct effect on color strength. Poorly dispersed pigments contain large agglomerates that behave like oversized particles, reducing effective surface area and light interaction. As a result, color appears weaker or duller.
Uniform dispersion allows pigment particles to absorb and scatter light efficiently, producing maximum chroma and accurate hue development. In color-critical applications, even small dispersion differences can lead to noticeable color deviation.
Color consistency and measurable color difference (ΔE) are therefore strongly linked to dispersion efficiency, particularly in high-performance organic pigments.
Influence on Gloss and Surface Appearance
Gloss is closely related to surface smoothness at the microscopic level. Poor dispersion leads to surface irregularities caused by pigment clusters protruding from the coating film. These irregularities scatter light, reducing gloss.
Well-dispersed pigments form a smoother, more uniform film surface, enabling specular reflection and higher gloss levels. This effect is especially important in applications such as automotive and industrial coatings, where visual quality is a key requirement.
Dispersion and Mechanical Performance
Beyond appearance, dispersion quality influences the mechanical properties of the final product. Agglomerated pigments can act as stress concentrators within a coating or plastic matrix, increasing the risk of cracking, abrasion, or premature failure.
Proper dispersion ensures that pigment particles are evenly embedded within the binder, contributing to improved film integrity, adhesion, and resistance to wear. This is particularly relevant in industrial coatings and engineering plastics exposed to mechanical stress.
Stability and Long-Term Performance
Dispersion quality also affects long-term stability. Poorly stabilized pigment systems may show sedimentation, flocculation, or color drift over time. These issues can compromise storage stability, application consistency, and end-use performance.
Effective stabilization through suitable dispersants and surface-treated pigments helps maintain a stable particle distribution, ensuring consistent performance throughout the product’s lifecycle.
For a broader explanation of pigment structure and particle behavior, see:
https://www.finelandchem.com/pigment-theory-and-color-science-training-session/
Factors Influencing Dispersion Quality
Several variables determine how well a pigment disperses in a given system:
-
Pigment particle size and surface characteristics
-
Type and amount of dispersant
-
Resin and solvent compatibility
-
Milling equipment and energy input
-
Formulation viscosity and pigment concentration
Optimizing dispersion requires balancing these factors to suit the specific pigment and application system.
Practical Implications for Industrial Applications
In industrial pigment applications, dispersion quality directly affects:
-
Color consistency between batches
-
Gloss and visual appearance
-
Mechanical durability and weather resistance
-
Processing efficiency and defect reduction
For high-performance pigments used in demanding environments—such as outdoor coatings or engineering plastics—dispersion quality can be as important as pigment chemistry itself.
Examples of pigments where dispersion control is critical include high-performance organic reds like Pigment Red 254, which rely on controlled particle distribution to deliver optimal color strength and durability.
Summary
Dispersion quality is a fundamental determinant of industrial pigment performance. From color strength and gloss to mechanical stability and long-term durability, the way pigments are dispersed within a formulation shapes the final outcome.
A clear understanding of dispersion principles enables formulators and technical teams to fully realize pigment potential, achieve consistent quality, and meet the performance demands of modern industrial applications.