A Comprehensive Overview for Sales, Procurement, and Technical Teams
On December 26, 2025, Fineland Chem held an in-depth training session on carbon black production processes and applications. This session provided our sales, procurement, and technical teams with essential knowledge on carbon black pigments, from general information to production techniques, and how its properties impact coatings. The training aimed to ensure all participants are equipped with the necessary understanding to assist customers and improve internal decision-making.
The session emphasized the technical aspects and practical applications of carbon black pigment (CBP), offering insights into its production methods and how its characteristics affect coating performance. By enhancing product knowledge across teams, we aim to improve our ability to deliver tailored solutions for customers globally.
General Information on Carbon Black Pigment
Carbon black is a fine black powder made from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons, widely used as a pigment in a variety of applications such as coatings, plastics, inks, and rubber products. It is primarily valued for its high color strength, opacity, and UV protection properties, making it an essential ingredient in many industrial and consumer products.
The forms of carbon black pigment vary depending on the production method, which influences its performance in different applications. The most common forms of carbon black pigment include dry beads, wet beads, and powder. Each form has its unique properties, making it suitable for specific use cases, such as automotive coatings, plastics, and printing inks.
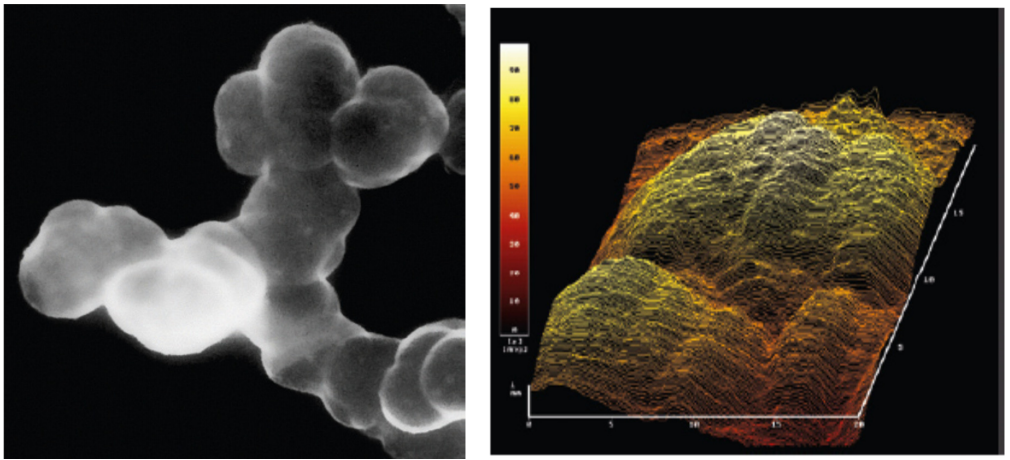
SEM Image of Carbon Black Pigment
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) provides a closer look at the fine particle structure of carbon black. The SEM image of carbon black pigment reveals the fine, solid particles that make up the pigment, along with their specific surface characteristics. This imaging technique helps in understanding how the pigment particles behave under various conditions, influencing their dispersibility, color strength, and stability in different systems.
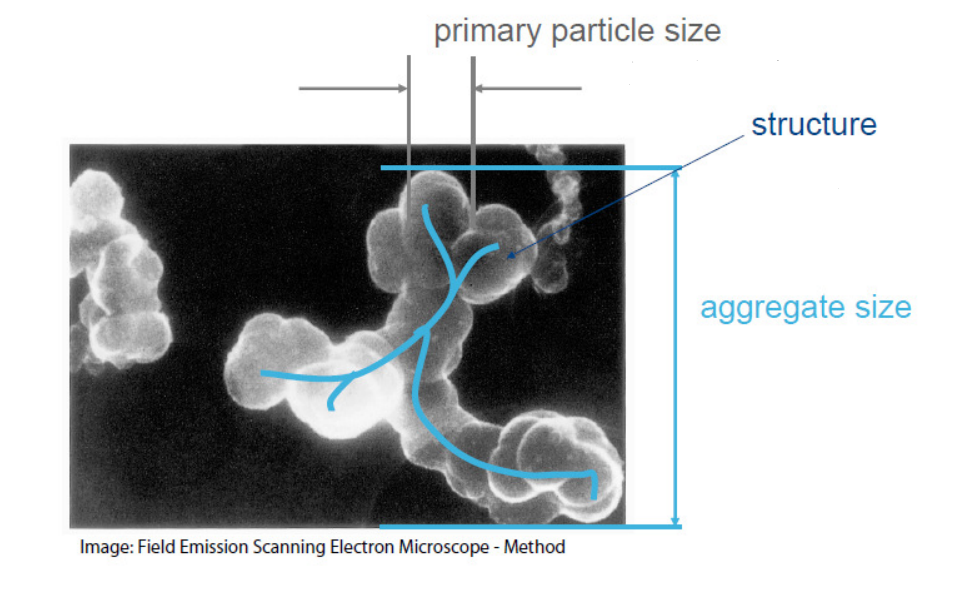
Primary Particles, Aggregates, and Structure
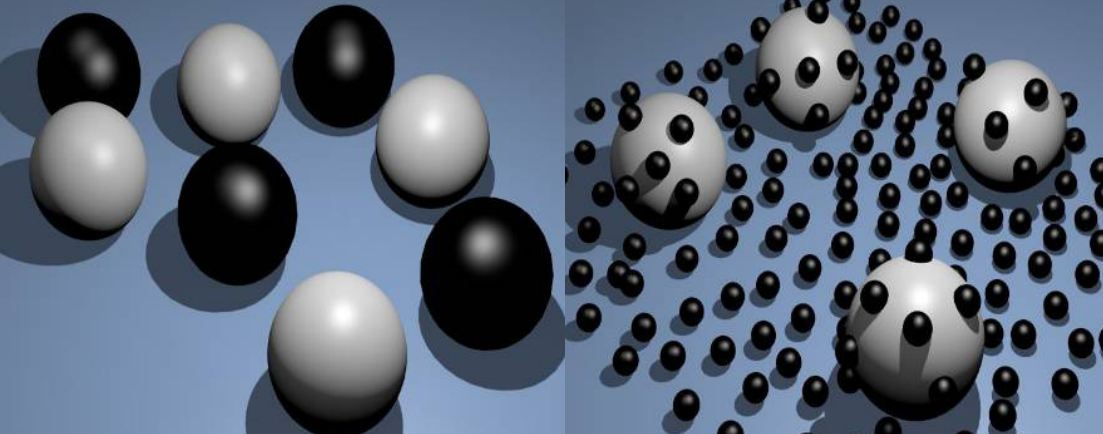
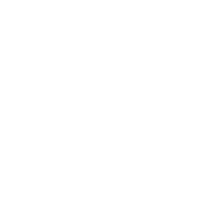
Carbon black is made up of primary particles, which are the individual, fine particles that form the core of the pigment. These primary particles then combine to form aggregates — clusters of particles that are fused together. Understanding the difference between primary particles, aggregates, and agglomerates is key to understanding how carbon black behaves in different formulations. The structure of carbon black influences its performance in applications, such as its dispersion quality, tinting strength, and ease of processing.
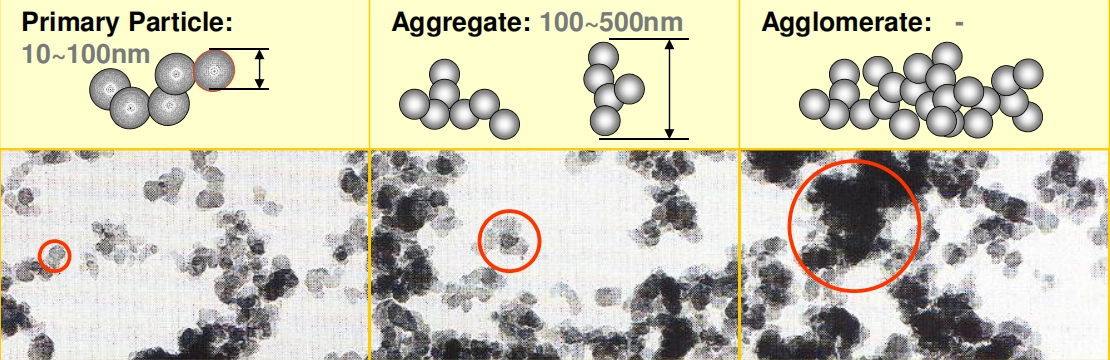
Primary Particles, Aggregates, and Agglomerates
When we look at carbon black’s morphology, it’s important to note that carbon black is a colloidal material. Agglomerates form when the aggregates combine together. These agglomerates, which are loosely bound, must be properly dispersed in the application process to maximize the pigment’s effectiveness. The primary particles determine the base quality of the pigment, while the agglomerates and aggregates can affect its dispersion properties and overall performance in various applications like coatings, inks, and plastics.
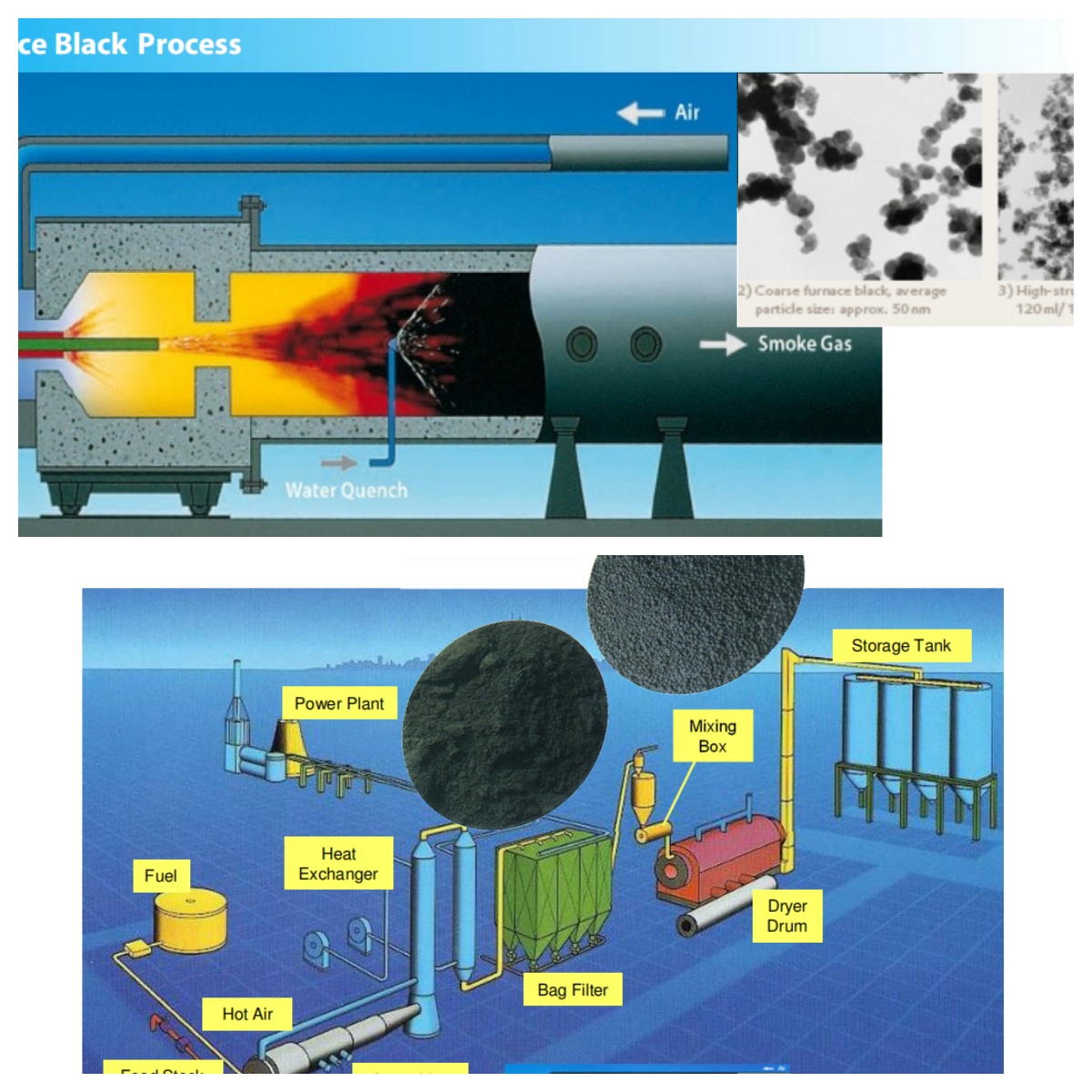
Production Process of Carbon Black
The production of carbon black involves combustion of hydrocarbon materials under controlled conditions to produce soot-like particles that are then processed into pigment. There are several methods of production, each producing carbon black with different characteristics suitable for various applications:
-
Furnace Black Process
The furnace black process is the most common and involves the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons at high temperatures. This process results in high-quality pigments with excellent color strength, dispersion, and low impurity levels. The carbon black produced through this method is ideal for applications requiring a deep black color and high-performance characteristics such as UV stability. -
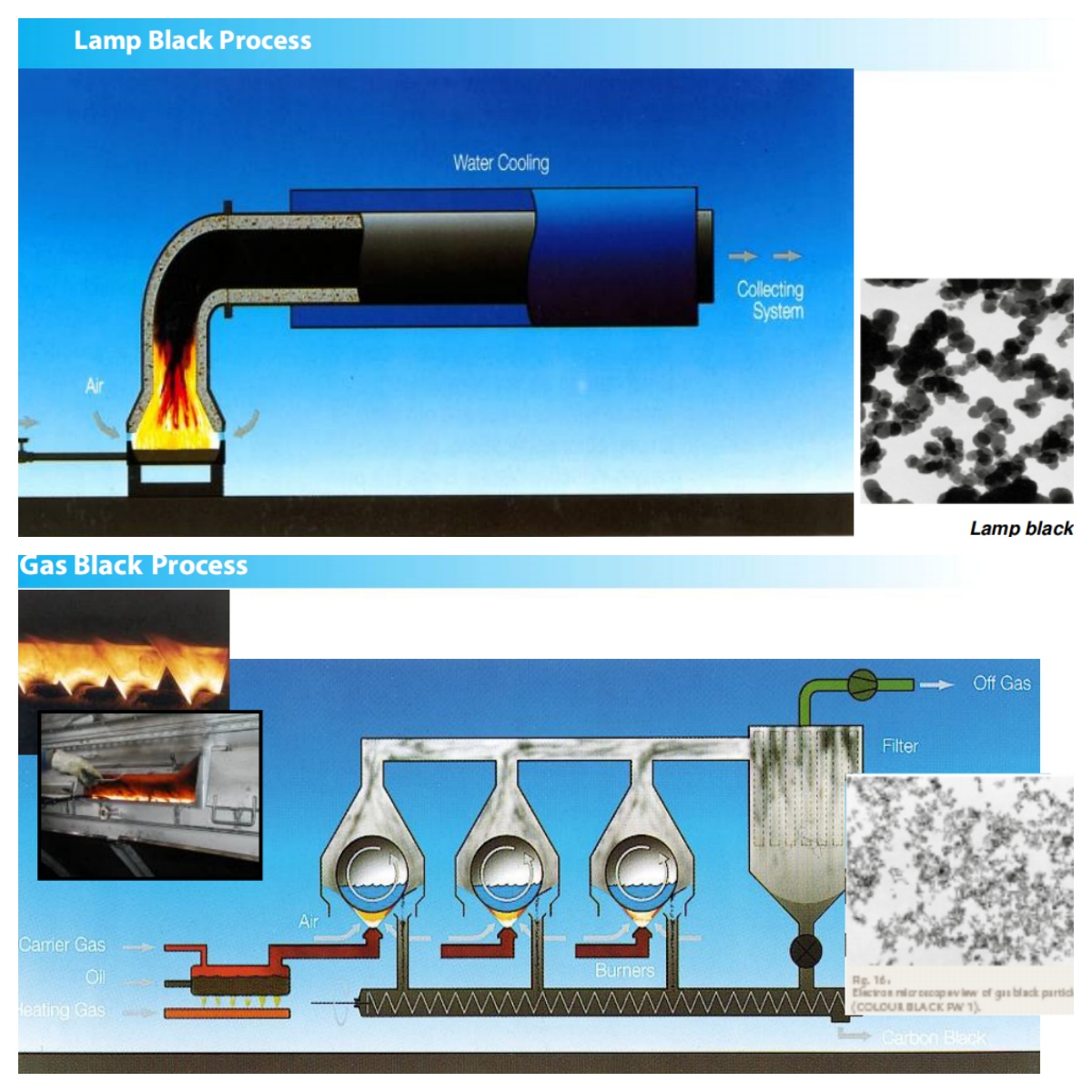
Lamp Black Process
An older method, the lamp black process, produces larger particle sizes and is used for specialized applications where a softer, less intense black pigment is desired, such as in art paints and decorative finishes. -
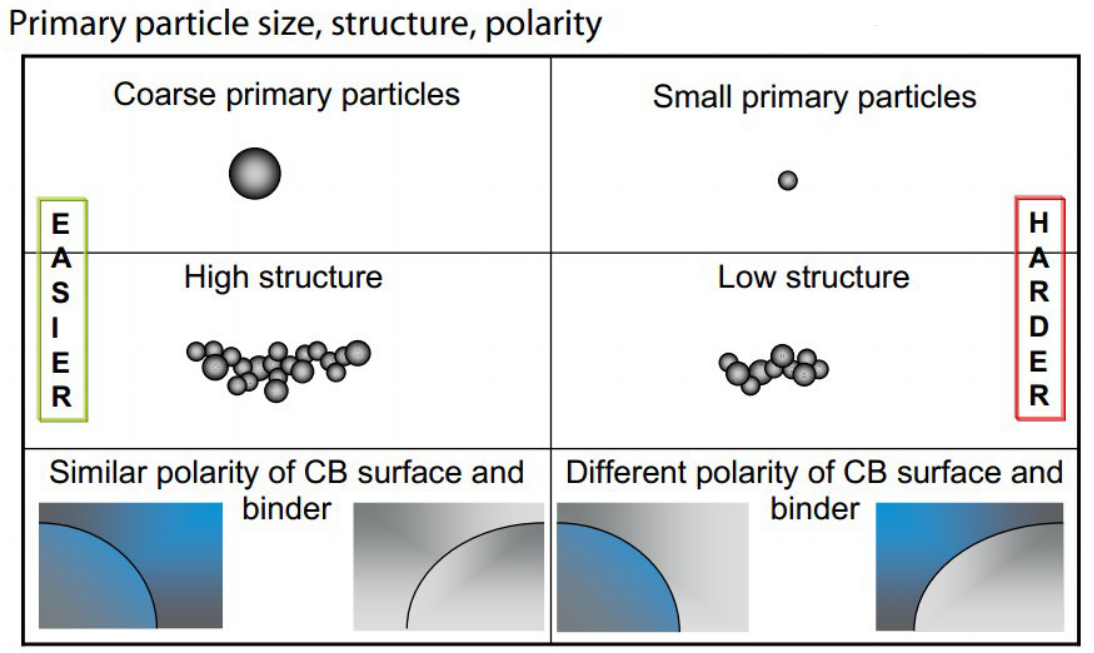
Gas Black Process
In the gas black process, natural gas or oil is partially oxidized to produce carbon black. This method results in fine particle size and is commonly used for applications that require high gloss and low viscosity. Gas black carbon black is often used in inks and plastics.
Understanding these production methods helps our teams explain to customers why specific grades of carbon black are best suited for their particular needs, and how particle size, surface treatment, and production methods affect performance in coatings.
Influence of Carbon Black Properties on Coating Performance
One of the key aspects discussed during the training was how the properties of carbon black pigments (CBP) influence coating performance. The dispersibility, color strength, and stability of carbon black all contribute significantly to the final quality of the coating.
-
Dispersibility
Proper dispersion of carbon black in resin systems is essential to achieving uniform color and excellent film formation. If carbon black is not well-dispersed, it can lead to poor color consistency and patchy finishes. Effective dispersion ensures that carbon black provides an even, durable layer of protection in coatings, reducing the risk of surface defects. -
Color Strength
The color strength of carbon black pigments directly impacts the opacity and depth of the coating. Higher color strength means better coverage, which is essential for coatings used in automotive exteriors, industrial finishes, and decorative coatings. The pigment’s ability to provide deep, consistent black contributes to both aesthetic appeal and functional performance. -
Lightfastness and Weathering Resistance
Carbon black’s lightfastness — its ability to resist fading under sunlight exposure — is a crucial attribute for coatings used in outdoor applications. The higher the lightfastness of carbon black, the longer the coating will maintain its original appearance, making it essential for automotive coatings and exterior finishes. Additionally, carbon black improves weathering resistance, helping coatings withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as UV radiation and moisture exposure.
By understanding these attributes, our sales and technical teams are better positioned to recommend the correct grade of carbon black for specific customer needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in coating applications.
Moving Forward: Building Expertise for Ongoing Success
At Fineland Chem, we are committed to continuous professional development and knowledge sharing. This training session is part of our broader initiative to ensure that our team is always well-informed and technically proficient in all aspects of the products we offer. By understanding the nuances of carbon black pigments, including their production processes and performance characteristics, we ensure that both our internal teams and customers can make informed, efficient decisions.
We will continue to provide training sessions and update our team on the latest trends and technical developments in the pigment industry, ensuring that Fineland Chem remains a leader in high-quality pigment solutions for the global market.